EVM Extensions - Staking & Distribution
Learn how to use Evmos EVM extensions to include Evmos and Cosmos SDK module functionalities in your smart contracts.
Stateful EVM Extensions on the core protocol allow dApps and users to access logic outside of the EVM. Acting as a gateway, these EVM Extensions define how smart contracts can perform cross-chain transactions (via IBC) and interact with core functionalities on the Evmos chain (e.g. staking, voting) from the EVM.
Note: Not sure what EVM extensions are? EVM extensions behave like smart contracts that are compiled and deployed within the EVM. If you are familiar with the EVM, you may know them as Precompiles. These have predefined addresses and, according to their logic, can be classified as stateful or stateless. When they change the state of the chain (transactions) or access state data (queries), extensions are considered "stateful"; when they don't, they're "stateless." Find a list of the available EVM extensions in the Evmos documentation.
This article presents a step-by-step guide to use the EVM extensions
corresponding to the staking and distribution modules.
With these we are able to stake tokens with our favorite validator
and withdraw staking rewards from the Evmos protocol using a smart contract.
Let's get started!
Prerequisites
- Know how to use Remix IDE.
Resources
You will need this material to code along:
- Remix IDE
- EVM extensions interfaces: Distribution.sol & Staking.sol
- EVM extensions common types and authorization interfaces: Types.sol & Authorization.sol:
- Example contract that uses the EVM extensions: SimpleStaker.sol
Use this link to open Remix with all the required files.
Approvals
Before executing certain transactions using the EVM Extensions, the user interacting with the smart contract must first approve these. This is a security measure, that is required to ensure that no unauthorized transactions can be executed on behalf of the user. In case of staking transactions, they should specify the amount allowed. The smart contract developer can choose to either separate the approval and execution of the EVM extensions transactions or to combine them into a single transaction.
We have provided convenient constants (e.g.: MSG_DELEGATE, MSG_UNDELEGATE),
that store the corresponding message type URLs required for the approval process.
This is done by calling the approve function, which will create an authorization grant for the given Cosmos SDK message.
The Simple Staker has the function approveRequiredMethods()
to perform the necessary approvals.
It approves the required methods for staking tokens (MSG_DELEGATE).
Step 1: Compile the contract
- Go to this link to open the Remix IDE with the necessary contracts
- Compile the
SimpleStakercontract with Remix
Step 2: Connect MetaMask to the Evmos testnet
Follow the corresponding guide on the Evmos docs to achieve this.
Step 3: Get some funds
If you don't have tEVMOS on your wallet, get some tokens from the Evmos Testnet Faucet.
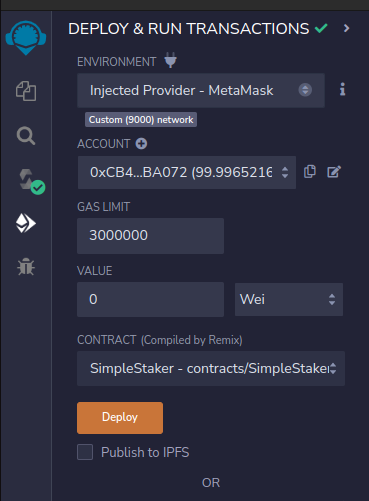
Step 4: Deploy the SimpleStaker.sol contract
- Go to Deploy & Run Transactions option on Remix's side bar
- Configure Injected Provider - MetaMask as the used environment
- Select the account with funds from the previous step
- Make sure the
SimpleStakercompiled contract is selected in the CONTRACT field - Deploy the smart contract by pressing the Deploy button & approving the transaction on Metamask
Upon a successful deployment, you should see the contract with its exposed methods being listed under Deployed Contracts.
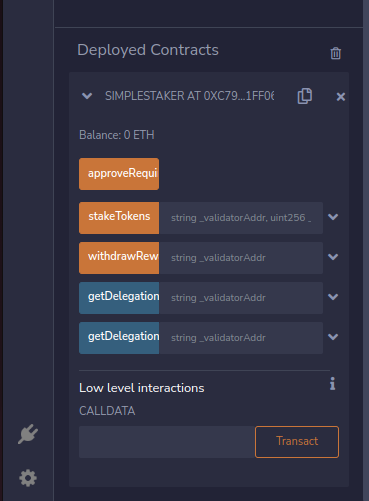
Step 5: Interact with the deployed contract
Get current validators
To use the SimpleStaker contract, we need a validator's address.
Check the current validators on our testnet Swagger API page or directly via REST at the /cosmos/staking/v1beta1/validators endpoint.
Copy the operator_address of the validator you want to use.
Use this as the _validatorAddr in the SimpleStaker functions.
Grant approvals
Before performing any transaction,
make sure to set the corresponding approvals.
To do so, call the approveRequiredMethods function.
This function will grant permissions to the smart contract
to use the MsgDelegate
on behalf of the caller.
Stake some tokens
Call the stakeTokens function using the validator address obtained previously
and the desired amount to stake.
Once the transaction is processed successfully,
you can check your current delegations calling the getDelegation function.
Additionally, you can check the current delegations using the Swagger API page where you use your Bech32-formatted address as the delegator.
Withdraw staking rewards
Proceed similarly with the withdrawRewards function to get your staking rewards.